
Newsroom
Probiotic Supplementation Modulates Toxicities of Aquatic Pollutant
Probiotic bacteria are known to improve the lipid metabolism activities by shifting gut microbiota, while aquatic pollutants will disturb gut microbial community and cause disorders in lipid metabolism.
It is obvious that probiotic bacteria and environmental pollutants can commonly target gut microbes and lipid metabolism. However, it remains unexplored whether administration of probiotic can modulate the toxic effects of aquatic pollutants.
A research team led by Dr. Lianguo CHEN from the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences exposed adult zebrafish to environmentally relevant concentrations of perfluorobutanesulfonate (PFBS), an aquatic pollutant of emerging concern, with or without dietary supplementation of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Interaction between PFBS and probiotic on microbial community composition and lipid metabolic dynamic was investigated across intestine, blood and liver tissues.
The researchers found that Lactobacillus genus correlated positively with other beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiota, thereby indirectly regulating host metabolic activities.
In female fish, the probiotic administration enhanced fatty acid synthesis and β-oxidation, but mitigated the accumulation of cholesterol in the blood caused by PFBS single exposure, highlighting the benefits of the probiotic to host health.
In male zebrafish, probiotic administration antagonized the PFBS-induced disturbances of bile acid metabolism, although coexposure to PFBS and probiotic caused significant accumulation of triglyceride in male livers, probably increasing the risk of hepatic steatosis.
For the first time, the present results demonstrated the sex-dependent modulation of probiotic bacteria on the toxic effects of PFBS pollutant, which can provide guidance to the application of probiotic supplements.
The study was published in Environmental Science & Technology.
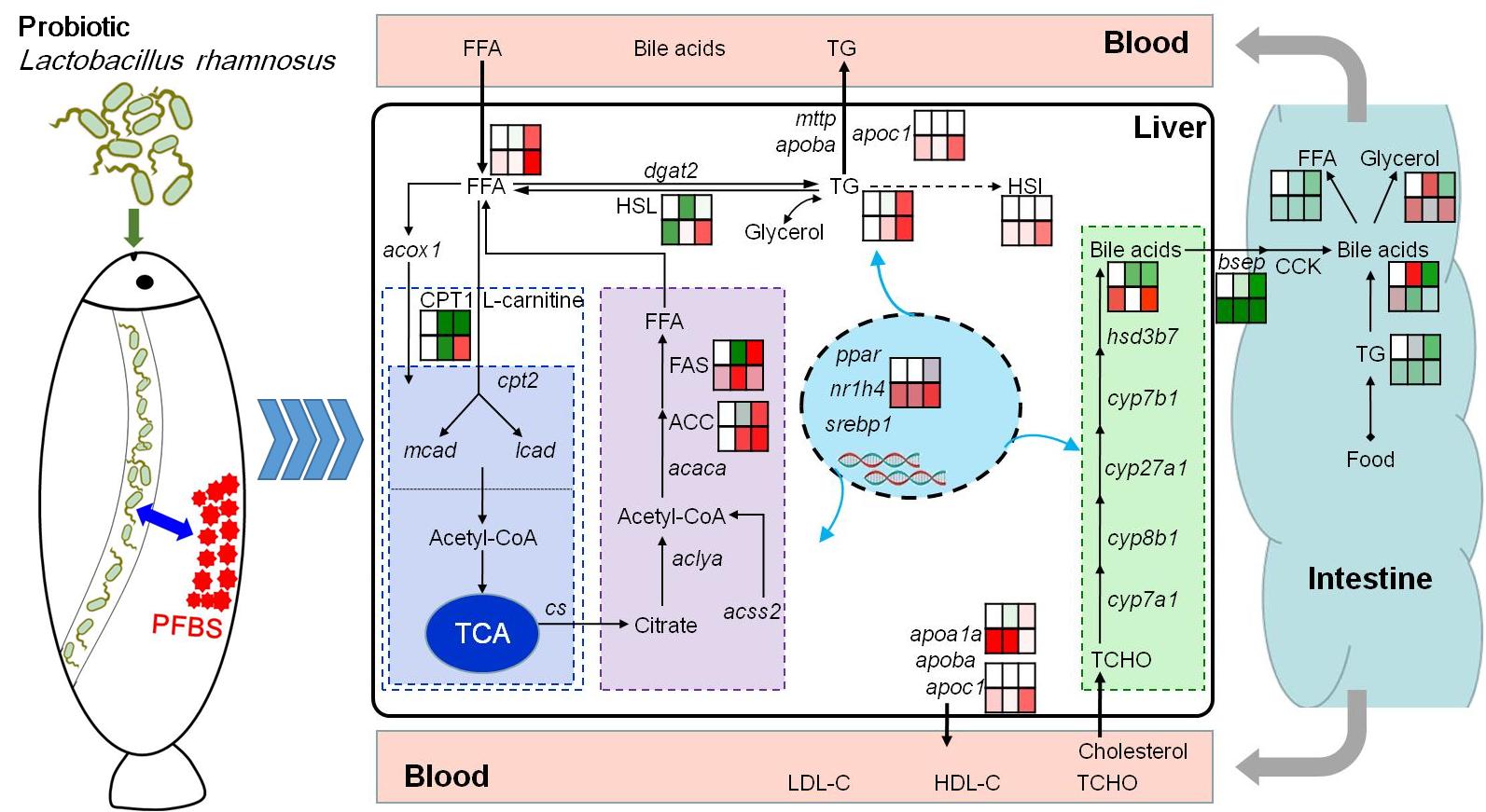
Probiotic administration modulates the lipid metabolic disorders of PFBS pollutant. (Image by IHB)